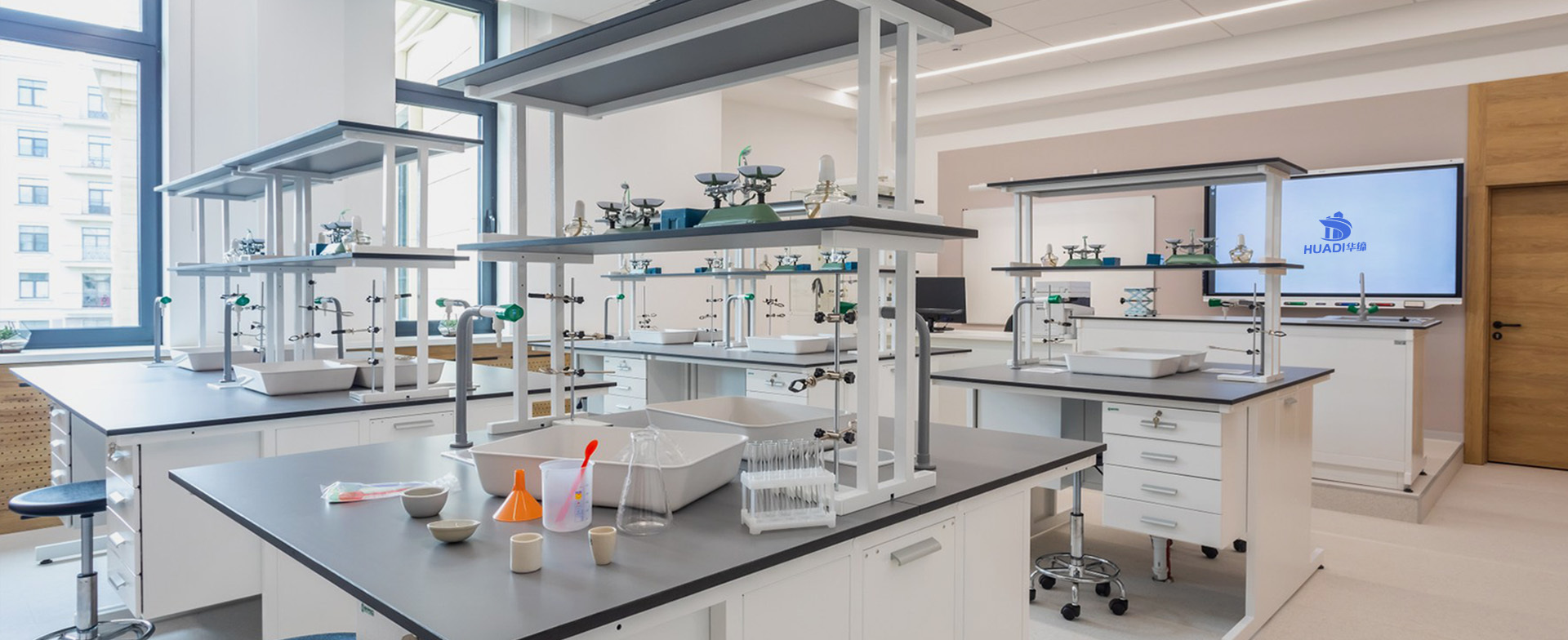
Centralized Water Supply System
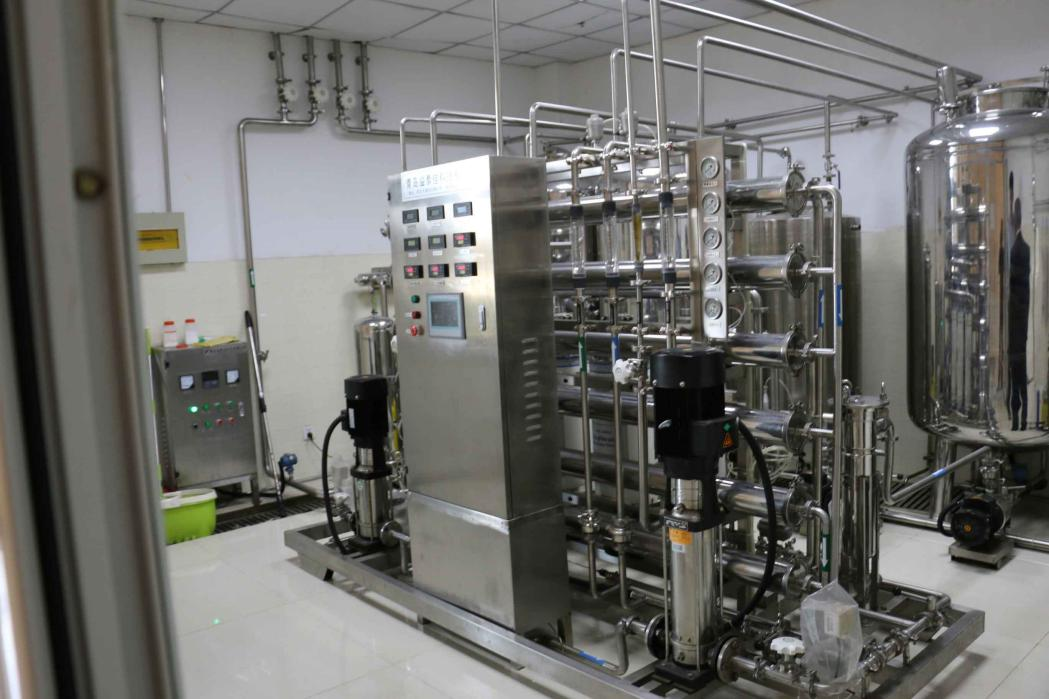 Laboratory pure water system is a kind of water with extremely high purity. It means that the conductive medium in the water is almost completely removed, and the non-dissociated gas, colloid and organic matter (including bacteria) are also removed to a very low level.
Laboratory pure water system is a kind of water with extremely high purity. It means that the conductive medium in the water is almost completely removed, and the non-dissociated gas, colloid and organic matter (including bacteria) are also removed to a very low level.
It adopts the combination of advanced reverse osmosis technology and ion exchange technology, and adopts microcomputer single-board computer program control. The water quality detection is automatically displayed, so as to obtain high-quality output water. Its output water resistivity can generally reach 18MΩ/cm. The booster pump, solenoid valve, high-capacity ion exchange resin, RO reverse osmosis membrane, filter element, pipeline connector, control original, ultraviolet lamp, etc. used in the equipment are all imported products. The reverse osmosis principle of ultrapure water machine is to apply a pressure greater than the natural osmotic pressure on the raw water side, so that the water molecules reverse osmosis from the high concentration side to the low concentration side. Because the pore size of the reverse osmosis membrane is much smaller than that of viruses and bacteria by hundreds or even thousands of times, various viruses, bacteria, heavy metals, solid soluble matter, polluted organic matter, calcium and magnesium ions, etc. cannot pass through the reverse osmosis membrane at all, thereby achieving the purpose of water purification.
Features of laboratory ultrapure water system:
(1) High working pressure and no water leakage: Since the module adopts rubber O-ring multi-layer sealing, it ensures that the module has high pressure resistance and no water leakage.
(2) No chemical substances are used: Since the concentrated water is filled with patented resin, the membrane resistance is reduced, so there is no need for concentrated water circulation and salt injection in the system. The resin is filled in the fresh water chamber in layers, which is more conducive to the removal of weak electrolytes.
(3) The system is simple and the piping is simple. Only 3 pipes (water inlet pipe, product water pipe and concentrated water pipe) are required. There is no circulation pump and salt injection system. No PLC program controller is required. The system construction cost and maintenance cost are low.
(4) Concentrated water recovery, the concentrated water quality (20-100 μ S/cm) is better than the raw water quality, and can be recycled for continued use before RO.
Using ion exchange method, the process is as follows: raw water → raw water booster pump → multi-media filter → activated carbon filter → water softener → precision filter → cation resin filtration → anion resin filtration → cation resin mixed bed → microporous filter → water point; using two-stage reverse osmosis method, the process is as follows: raw water → raw water booster pump → multi-media filter → activated carbon filter → water softener → precision filter → first-stage reverse osmosis → PH adjustment → intermediate water tank → second-stage reverse osmosis → purified water tank → pure water pump → microporous filter → water point; using EDI method, the process is as follows: Laboratory ultrapure water system, ultrapure water equipment raw water → raw water booster pump → multi-media filter → activated carbon filter → water softener → precision filter → primary reverse osmosis machine → intermediate water tank → intermediate water pump → EDI system → microporous filter → water point; raw water → multi-media filter → activated carbon filter → water softener → intermediate water tank → low-pressure pump → PH value adjustment → high-efficiency mixer → precision filter → high-efficiency reverse osmosis → intermediate water tank → EDI water pump → EDI system → microporous filter → water point To understand the principle of reverse osmosis desalination, you must first understand the concept of "permeation". Permeation is a physical phenomenon. When two waters containing different concentrations of salt are separated by a semi-permeable membrane, it will be found that the water on the side with less salt content separates and penetrates through the membrane into the water with higher salt content, while the salt contained does not penetrate. In this way, the salt concentration on both sides is gradually blended to an equal level. The
centralized water supply system generally includes a host, a pipeline system, and a terminal.