Animal Room Laboratory System
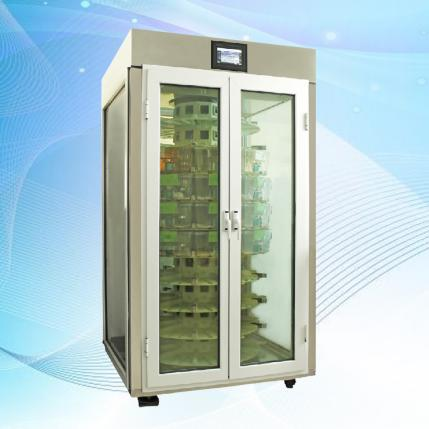 The design of animal house laboratories needs to comprehensively consider functionality, safety, comfort, compliance and sustainability. Key elements include site selection and layout, ventilation and air purification systems, sound insulation and shock absorption measures, animal breeding environment, safety protection facilities and data management systems. Design strategies recommend the use of flexible design, humanized design, animal-friendly design, intelligent design, energy-saving and environmental protection design and safety design.
The design of animal house laboratories needs to comprehensively consider functionality, safety, comfort, compliance and sustainability. Key elements include site selection and layout, ventilation and air purification systems, sound insulation and shock absorption measures, animal breeding environment, safety protection facilities and data management systems. Design strategies recommend the use of flexible design, humanized design, animal-friendly design, intelligent design, energy-saving and environmental protection design and safety design.
Animal house laboratories are important places for life science research, biomedical development and animal model experiments. Designing a laboratory that meets specifications, meets needs and pays attention to animal welfare is of great significance to ensuring research quality, improving scientific research efficiency and maintaining animal health.
Design goals and principles
1. Functionality: Ensure that the laboratory meets various scientific research needs, such as animal husbandry, experimental operations, data analysis, etc.
2. Safety: Ensure the safety of staff and animals, prevent the spread of pathogens and accidents.
3. Comfort: Provide animals with a suitable living environment, reduce stress reactions, and improve animal welfare. 4. Compliance
: Comply with relevant domestic and international laws and regulations and standards to ensure the compliance of the laboratory.
5. Sustainability: Adopt environmentally friendly and energy-saving design solutions to reduce the impact of the laboratory on the environment.
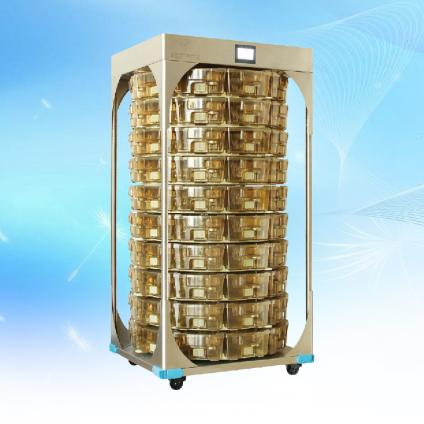 Key design elements
Key design elements
1. Site selection and layout
The site should be far away from pollution sources and have good natural conditions and convenient transportation. The laboratory layout should follow the workflow and reasonably divide functional areas, such as animal breeding area, experimental operation area, disinfection area, etc. There should be clear separation between the areas to avoid cross contamination.
2. Ventilation and air purification system
Design an independent ventilation system to ensure air circulation in each area and reduce the risk of pathogen transmission. Use high-efficiency filters and ultraviolet disinfection devices to purify and disinfect the air. At the same time, consider installing an exhaust system to remove harmful gases and odors in time.
3. Sound insulation and shock absorption measures
To reduce the impact of noise and vibration on animals, effective sound insulation and shock absorption measures should be taken. For example, use sound insulation materials, shock absorbers, etc. to ensure that the internal environment of the laboratory is quiet and stable.
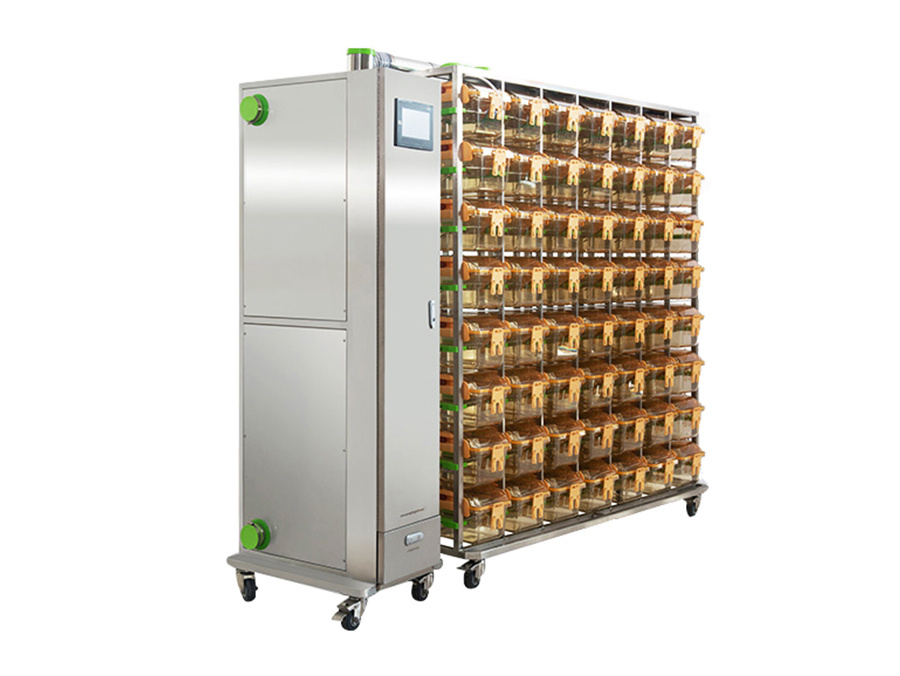
4. Animal breeding environment
Pay attention to animal welfare and provide animals with a suitable breeding environment. For example, control indoor temperature, humidity, light and other conditions, provide comfortable cages and feeding systems, set up appropriate activity space, etc.
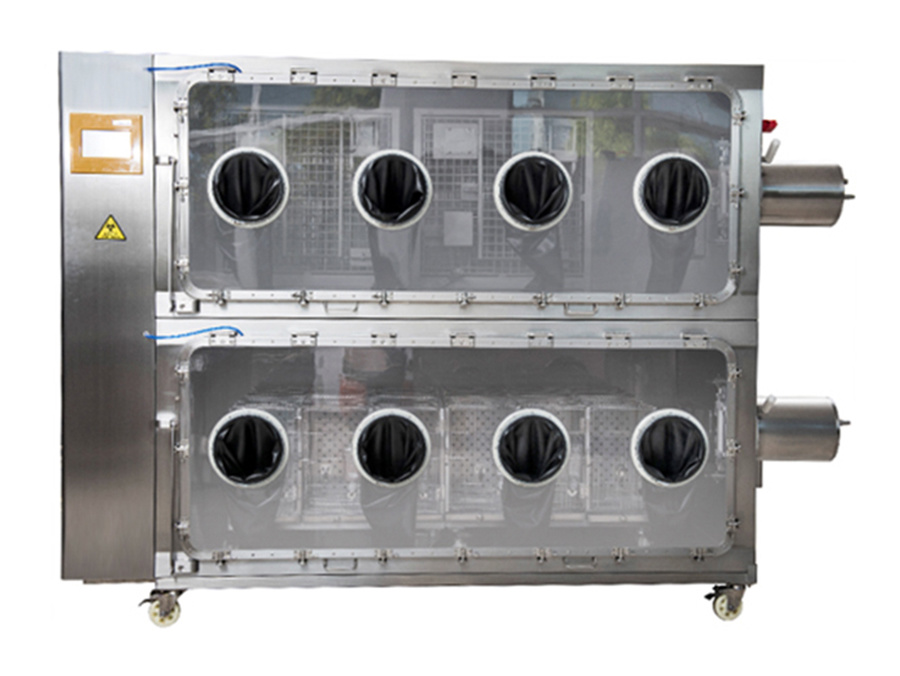
5. Safety protection facilities
are equipped with necessary safety protection facilities, such as isolators, biosafety cabinets, emergency eyewashes, etc., to ensure the safety of staff and animals. At the same time, set up obvious safety warning signs and safety passages to facilitate rapid evacuation in emergency situations.
6. Data management system
Establish a complete data management system, including storage and analysis functions for experimental records, animal information, equipment usage, etc. Use an electronic management system to improve work efficiency and data accuracy.